Material Performance Chart
METALLIC (STEEL & ALUMINUM)
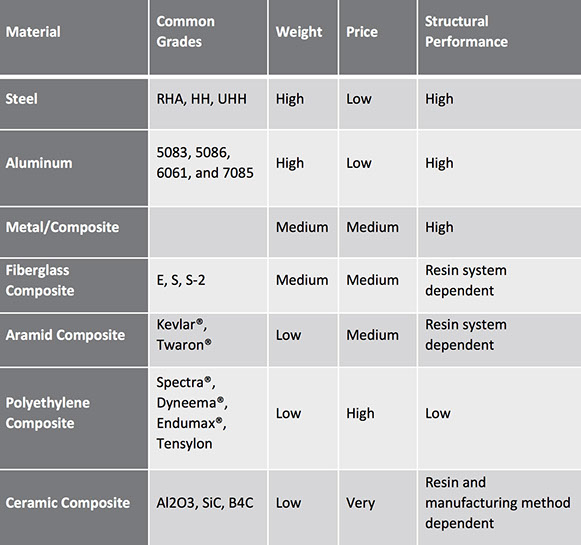
Steel and aluminum alloys are used commonly when weight is not the driving requirement for the armor. Metallics are traditionally the lowest cost and heaviest solution. The hardness and specific chemical composition of these materials play a key role in their contribution to stopping the incoming projectile. Cost, weight, and the ability to fabricate will vary by alloy.
COMPOSITE ARMOR MATERIALS (FIBERGLASS, ARAMID, AND POLYETHYLENES)
Composites are available in a wide variety of forms and configurations with varying performance, cost and weight. The properties of composites are largely dependent on the fiber, the resin and the way the materials are processed. Composite materials provide a weight saving over metallic solutions, but result in an increased cost.
CERAMICS
Ceramic materials are used when a low weight solution is needed for higher level threat protection. Ceramics are typically used in combination with metallic and composite materials. Ceramics vary in cost and availability. The most common types found in ballistic applications are alumina oxide (Al2O3), silicon carbide (SiC), and boron carbide (B4C).